The Basics of Garment Manufacturing: An Overview
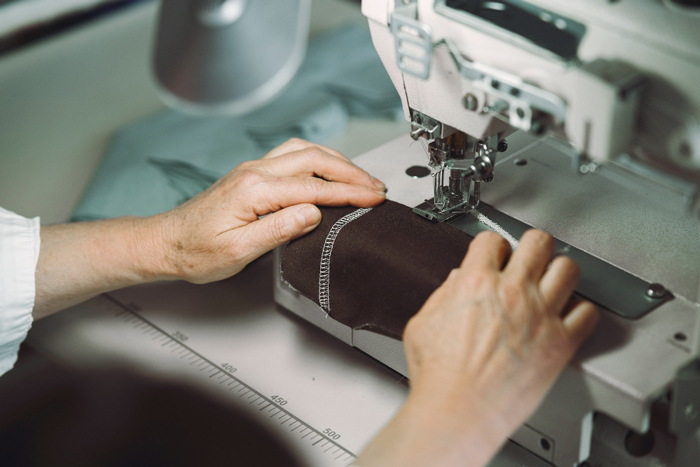

Table of Contents
ToggleIn the fast-paced world of fashion, understanding the basics of garment manufacturing is essential for success. Whether you’re a fashion enthusiast, a budding entrepreneur, or a student in the fashion industry, having a solid grasp of the garment manufacturing process is crucial. This comprehensive overview will guide you through each stage of garment manufacturing, highlighting key considerations and best practices.
I. Design and Development Stage
A. Conceptualizing the Design:
At the heart of garment manufacturing is the design phase. It begins with translating design ideas into sketches or digital renderings. Fashion designers draw inspiration from various sources, including fashion trends, cultural influences, and customer preferences. This stage involves brainstorming, sketching initial concepts, and refining the chosen design.

B. Pattern Making:
Pattern making is the next crucial step in garment manufacturing. Patterns are the blueprints that guide the construction of the garment. Pattern makers create precise templates using measurements, style lines, and design details from the original design. This stage requires expertise in geometry, mathematics, and garment construction techniques.

C. Sample Development:
Sample development is the process of creating prototypes to test the design, fit, and functionality of the garment. It involves translating the patterns into actual fabric pieces, which are then sewn together to form the first sample. Multiple iterations are often necessary to achieve the desired fit and aesthetic.
II. Fabric and Materials
A. Fabric Selection:
Choosing the right fabric is essential for the success of any garment. Factors such as durability, comfort, drape, and desired aesthetic impact the fabric selection. Common fabric types include cotton, silk, polyester, and various blends. Designers and manufacturers need to consider the properties of each fabric type and how they align with the intended garment.
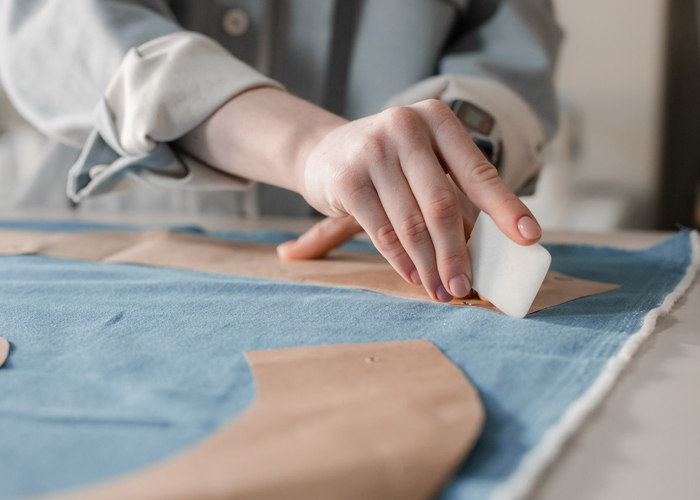

B. Fabric Sourcing:
Once the fabric type is determined, sourcing high-quality materials becomes crucial. Garment manufacturers establish relationships with reliable fabric suppliers, ensuring consistency in quality and adherence to industry standards. Factors such as cost, availability, lead time, and environmental sustainability are taken into account when selecting fabric suppliers.
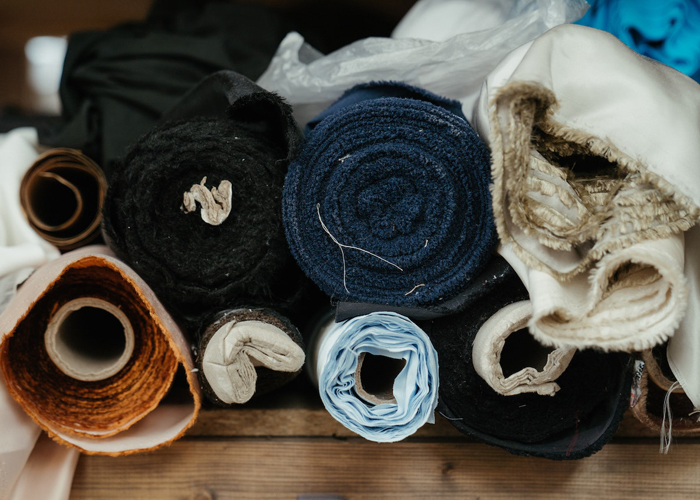

C. Trims and Accessories:
Trims and accessories, such as buttons, zippers, ribbons, and labels, add functional and decorative elements to the garment. Selecting appropriate trims and accessories is crucial to achieving the desired aesthetic and ensuring garment functionality. Factors considered include durability, style, cost, and compatibility with the fabric and design.
III. Production Planning and Processes
A. Cutting and Marking:
Once the design, patterns, and fabric are ready, the cutting and marking stage comes into play. Fabric is prepared by laying it out and marking the pattern pieces accurately. Specialized cutting machines or skilled cutters with manual tools are used to cut the fabric precisely, ensuring minimal waste and accurate pattern replication.
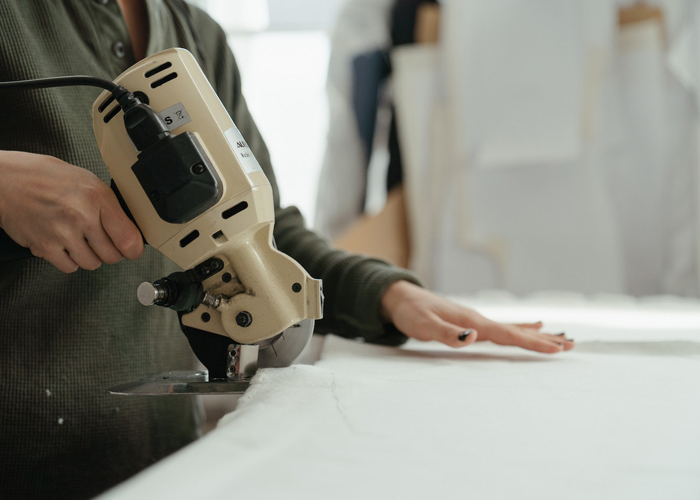

B. Sewing and Assembly:
Sewing and assembly is the core stage of garment manufacturing. This stage involves organizing the assembly line, training skilled operators, and implementing standardized sewing techniques. The goal is to ensure efficient production flow, consistent quality, and timely completion of each garment.
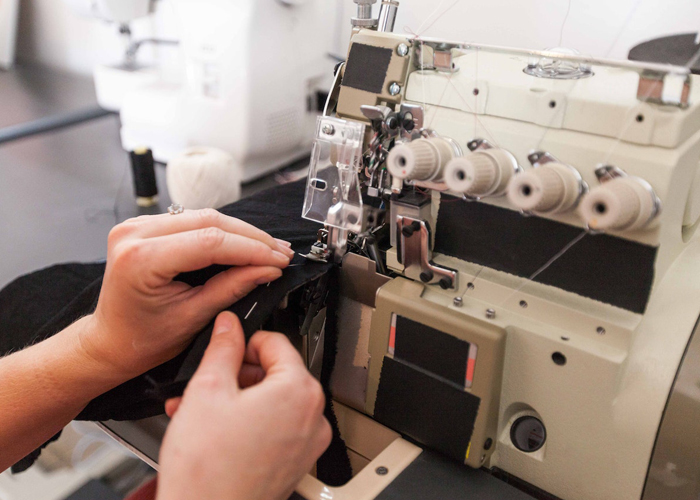

C. Finishing and Quality Control:
After the sewing process, the garment enters the finishing stage. Finishing touches such as stitching, pressing, trimming loose threads, and attaching labels are applied. Quality control plays a crucial role in this stage, where garments undergo inspections to ensure they meet the desired quality standards. Any defects or imperfections are identified and addressed before packaging.

IV. Production Management and Logistics
A. Supply Chain Management:
Effective supply chain management is essential for the smooth operation of garment manufacturing. It involves coordinating with suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors to ensure the timely delivery of materials and finished garments. Clear communication, accurate forecasting, and establishing strong relationships are key factors for success.
B. Production Capacity and Lead Time:
Calculating production capacity and managing lead time is vital to meet customer demands and deadlines. Manufacturers must optimize efficiency by balancing production volume, labor availability, and machine capacity. Accurate production planning, streamlined processes, and effective resource allocation are crucial for meeting production targets.
C. Cost Control and Budgeting:
Managing costs and budgeting effectively is necessary for the profitability of garment manufacturing. Manufacturers need to monitor production costs, including raw materials, labor, overheads, and logistics. Identifying areas for cost-saving, negotiating favorable terms with suppliers, and implementing efficient production practices contribute to overall cost control.

V. Compliance and Ethical Considerations
A. Environmental Sustainability:
Garment manufacturers are increasingly embracing sustainable practices to minimize their environmental impact. This involves using eco-friendly materials, reducing waste through recycling and upcycling, and adopting energy-efficient production processes. Sustainable certifications and compliance with environmental regulations are becoming essential considerations.
B. Worker Welfare and Labor Standards:
Ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and ethical labor practices is paramount in garment manufacturing. Manufacturers must comply with local and international labor laws and adhere to industry standards. Regular audits, social compliance programs, and fostering a positive work environment contribute to worker welfare and ethical manufacturing practices.
Conclusion:
Understanding the basics of garment manufacturing provides valuable insights into the complex processes involved in bringing fashion designs to life. By grasping the design and development stage, fabric and material considerations, production planning and processes, production management and logistics, and compliance and ethical considerations, you are equipped with the knowledge to navigate the garment manufacturing industry successfully. Attention to detail, quality control, and adherence to sustainability and ethical practices contribute to creating garments that meet the demands of the market while upholding industry standards. Continual learning and adaptation are essential to thrive in this ever-evolving industry.