Exploring Different Types of Garment Production Techniques

Table of Contents
ToggleThe world of fashion and clothing manufacturing is an ever-evolving landscape that constantly seeks innovative techniques, incorporates technological advancements, and embraces sustainability initiatives. In this comprehensive article, we will embark on an in-depth exploration of the various garment production techniques, ranging from traditional methods rooted in craftsmanship to modern approaches driven by automation and digitization. We will examine the strengths and limitations of each technique, as well as their impact on the fashion industry’s sustainability efforts.
I. Traditional Garment Production Techniques
1- Handcrafted Techniques
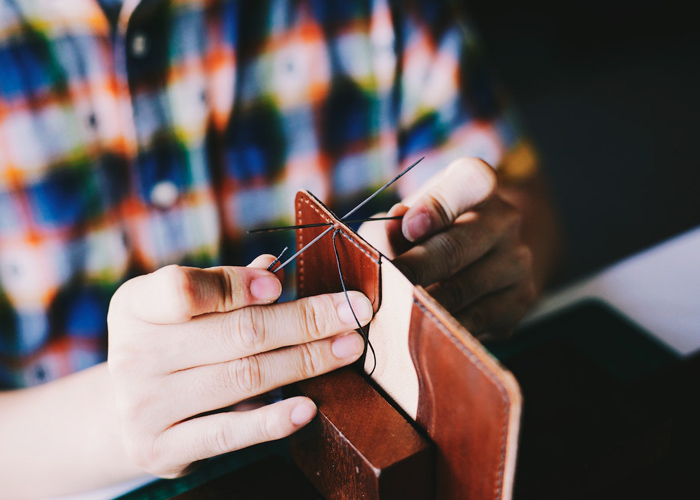
Sewing by hand: Hand sewing is an ancient art that involves using a needle and thread to create garments with meticulous precision. This method allows skilled artisans to create exquisite, one-of-a-kind pieces, often infused with a sense of artistry and personal touch that sets them apart from mass-produced items. Hand-sewn garments are especially sought-after for their attention to detail and unique embellishments.

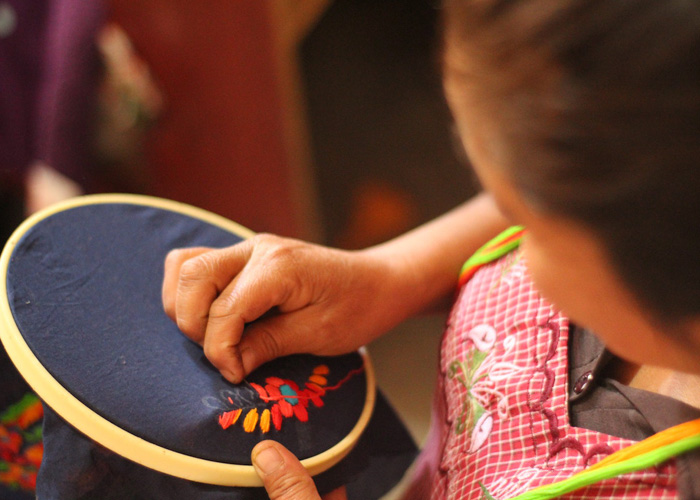
Embroidery: Embroidery is the art of decorating fabric using needle and thread or yarn to create intricate patterns, motifs, and designs. Skilled embroiderers can add embellishments to garments, enhancing their aesthetic appeal and adding a touch of luxury. Hand-embroidery, in particular, holds cultural significance in various regions around the world, preserving traditional craftsmanship and cultural heritage.

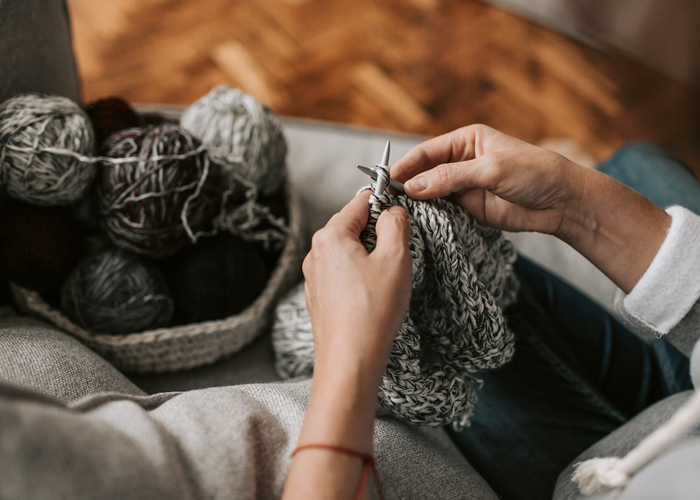
Knitting and Crochet: Knitting and crochet techniques involve creating fabric by interlocking loops of yarn with needles or hooks. These traditional methods offer versatility in creating various textures and patterns, resulting in cozy, warm garments such as sweaters, scarves, and shawls. Knitted and crocheted items are often cherished for their comfort and ability to evoke feelings of nostalgia.

2- Tailoring
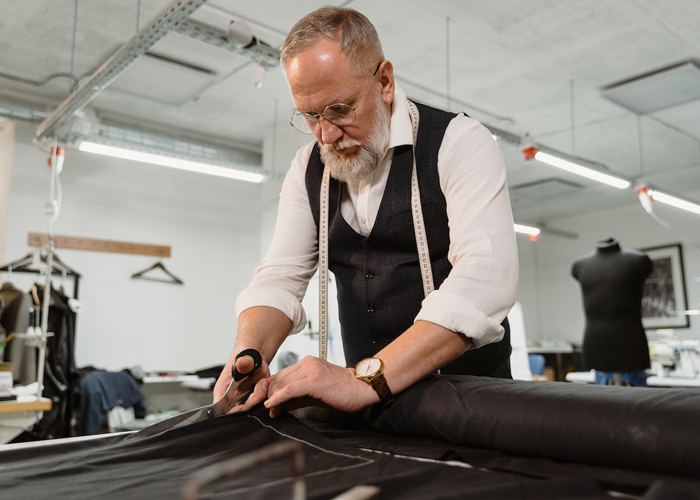
Bespoke Tailoring: The epitome of personalized fashion, bespoke tailoring involves creating made-to-order garments tailored precisely to an individual’s measurements, body shape, and style preferences. This meticulous process ensures a perfect fit and a garment that flatters the wearer’s unique physique. Bespoke tailoring often requires multiple fittings and consultations with skilled tailors, resulting in exclusive and luxurious pieces.

Made-to-Measure: Made-to-measure garments offer a balance between ready-to-wear and bespoke, using pre-existing patterns adjusted to fit individual measurements. This approach allows for a higher degree of customization compared to off-the-rack clothing, catering to customers with specific size requirements and style preferences. Made-to-measure garments strike a balance between personalization and affordability.
II. Mechanized Garment Production Techniques
1- Mass-Production
Assembly Line: Mass-production revolutionized the garment industry by introducing an assembly line approach, where garments are manufactured in stages with different specialized workers performing specific tasks. This method significantly increased production efficiency, allowing for large quantities of garments to be produced rapidly and cost-effectively. However, the downside of mass production lies in its potential for creating standardized, cookie-cutter designs and the risk of worker exploitation in some cases.

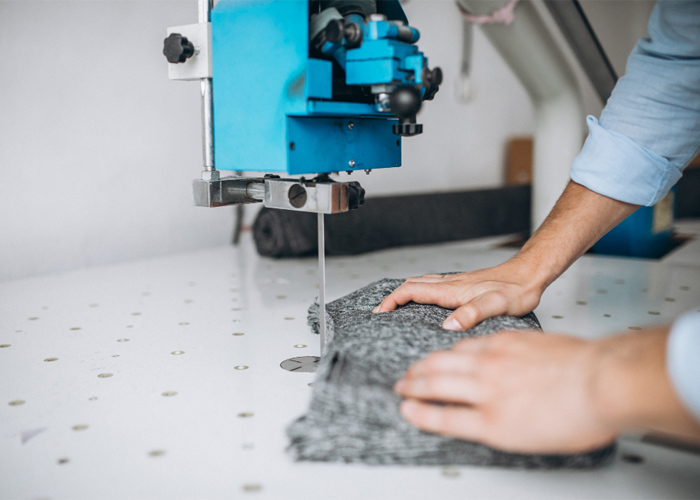
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Cutting: Automated cutting systems driven by computer programs have revolutionized fabric cutting. CNC machines use digital patterns to precisely cut fabric layers, minimizing waste and ensuring uniformity in garment components. This technology significantly speeds up the cutting process, reducing production time and costs while promoting accuracy and consistency.

2- Sewing Machines
Single Needle Sewing Machine: The single-needle sewing machine is a fundamental tool in garment production, used for stitching seams, attaching buttons, and creating simple designs. This versatile machine allows for efficient stitching, making it an indispensable part of both small-scale and large-scale manufacturing. While single-needle machines enhance productivity, they still require skilled operators to ensure quality stitching and finishing.
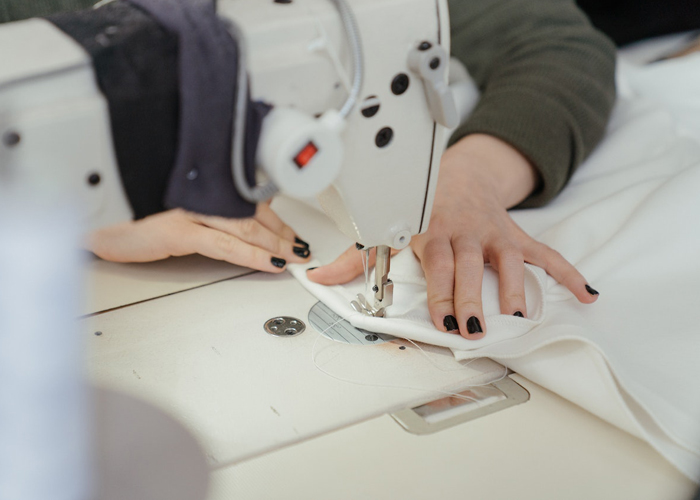

Overlock Machine: The overlock machine, also known as a serger, is used to create professional seam finishes that prevent fabric fraying. This machine is commonly employed in the production of knitwear and stretch fabrics, where neat and durable edges are essential. Overlock machines contribute to the longevity and durability of garments, reducing the likelihood of unraveled seams.
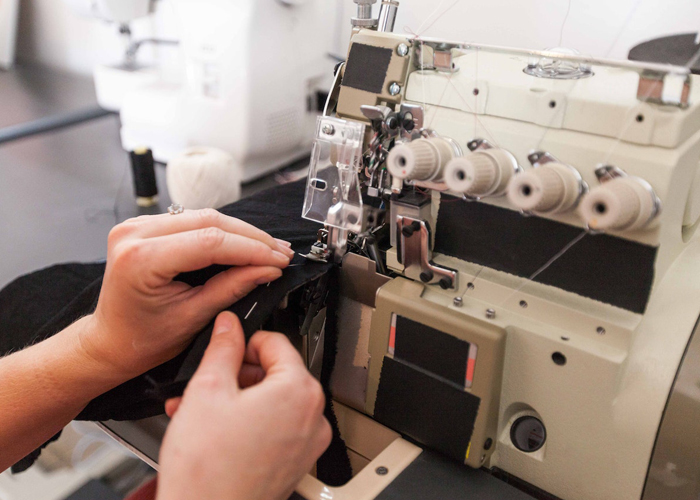

Cover Stitch Machine: Cover Stitch machines are used for hemming and topstitching, particularly in activewear and knit garments. This machine creates two or three rows of parallel stitching on the top of the fabric, with a looped stitch on the back, resulting in a stretchable and flexible seam. Cover Stitch machines are critical in providing a polished and professional finish to hems and top edges.

III. Advanced Garment Production Techniques
1- 3D Printing
Fabric and Textile Printing: 3D printing has expanded its applications into fabric and textile printing, allowing designers to create intricate patterns and designs directly on fabric. This technology opens up new avenues for creative expression and customization, enabling garments with complex and unique textures. Additionally, 3D printing on fabric reduces the need for additional trims and embellishments, making the design process more sustainable.
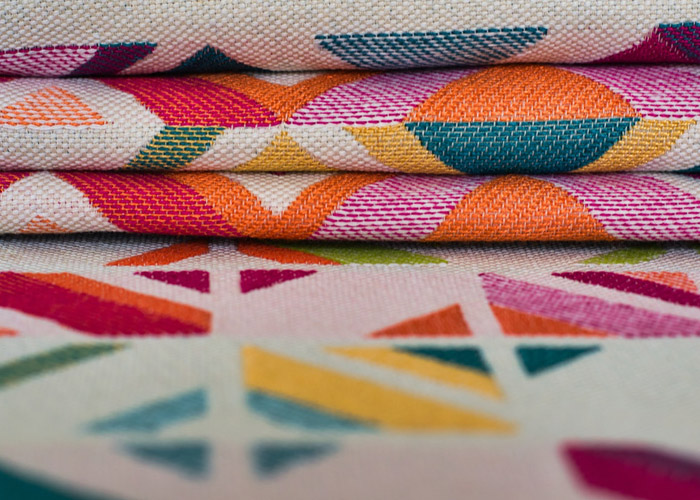

Accessory Production: 3D printing has also revolutionized accessory production within the fashion industry. Designers can now create buttons, zippers, buckles, and other garment components using 3D printing techniques, facilitating innovative and sustainable designs. Moreover, 3D-printed accessories can be easily customized, allowing for greater personalization and reduced waste.

2- Laser Cutting
Precise Cutting: Laser cutting is a precise and efficient technique used to cut fabric layers accurately. Laser technology ensures that intricate patterns and designs can be cut with exceptional detail, reducing the need for manual cutting and minimizing fabric waste. This method has gained popularity in high-end fashion, as it allows designers to push the boundaries of creativity while maintaining a sustainable approach.
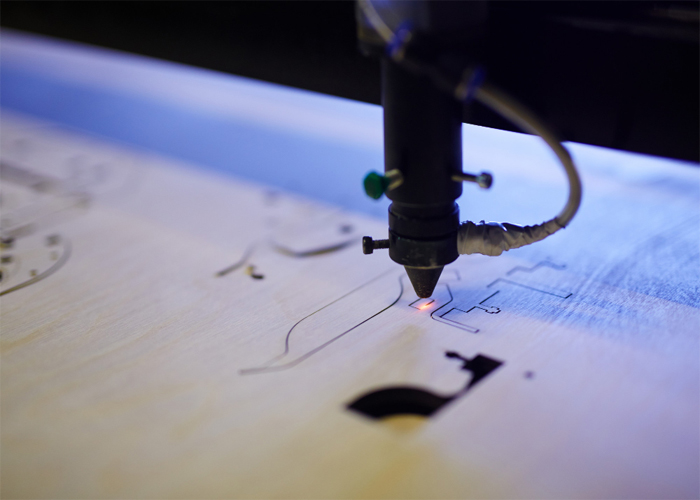
Appliqué and Engraving: Laser cutting machines can also be used to create appliqués and engravings on garments, adding intricate details and embellishments. Appliqués made through laser cutting provide a seamless and refined finish, enhancing the overall aesthetic of the garment. Additionally, laser-engraved patterns and designs add a unique and personal touch to apparel.
3- Digital Printing
Direct-to-Garment Printing: Digital printing, specifically direct-to-garment (DTG) printing, is a revolutionary technology that enables high-resolution printing directly onto fabric. This process involves applying water-based inks to the garment, allowing for vibrant and detailed designs without the need for screen setups. DTG printing is eco-friendly, as it produces minimal waste and uses environmentally friendly ink formulations.

Sublimation Printing: Sublimation printing is another digital printing technique that transfers dye onto fabric using heat. The dye sublimation process results in vibrant, long-lasting prints that do not fade or crack, making it an ideal method for sportswear and activewear. Sublimation printing offers the advantage of producing full-color designs with intricate details, showcasing the potential for creative expression in the fashion industry.
IV. Sustainable Garment Production Techniques
1- Eco-Friendly Fabrics
Organic Cotton: Organic cotton cultivation follows strict guidelines that prohibit the use of synthetic pesticides and genetically modified seeds. By opting for organic cotton, the fashion industry reduces its environmental impact and supports farmers’ health and livelihoods. Garments made from organic cotton are hypoallergenic, breathable, and biodegradable, making them an eco-conscious choice for consumers.
Tencel/Lyocell: Tencel, also known as Lyocell, is a sustainable fiber derived from wood pulp, primarily sourced from eucalyptus or beech trees. The production of Tencel involves a closed-loop process that recycles and reuses solvents, minimizing waste and water usage. Tencel fabrics are soft, durable, and biodegradable, making them an eco-friendly alternative to conventional textiles.
Recycled Polyester: Recycled polyester is produced by converting post-consumer plastic bottles into polyester yarn. This process diverts plastic waste from landfills and reduces the demand for petroleum-based virgin polyester. Recycled polyester fabrics offer the same quality and performance as conventional polyester while promoting circular economy practices within the fashion industry.
2- Zero-Waste Techniques
Pattern Making: Zero-waste pattern making focuses on designing garments in a way that minimizes fabric waste during production. Designers strategically arrange pattern pieces to utilize the entire fabric without generating offcuts or scraps. This approach not only reduces textile waste but also challenges designers to think creatively and optimize material usage.
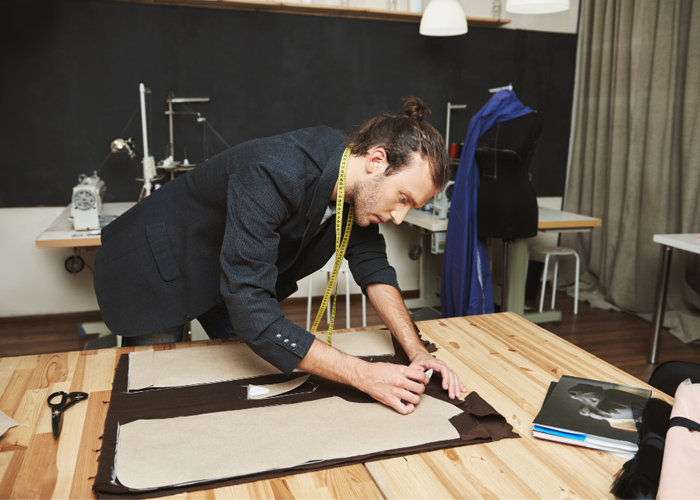

Upcycling: Upcycling involves transforming discarded or unused materials into new garments or accessories. Designers can repurpose vintage clothing or surplus fabrics to create unique and eco-friendly fashion pieces. Upcycling celebrates creativity and sustainability, breathing new life into old textiles that might otherwise end up in landfills.
3- On-Demand Production
Customization: On-demand production embraces the concept of customization, allowing customers to personalize their garments according to specific preferences, sizes, and styles. By producing clothing only when ordered, this approach minimizes excess inventory and reduces the potential for unsold stock, thereby decreasing overall waste.
Made-to-Order: Made-to-order production aligns with on-demand principles, where garments are manufactured based on customer specifications and measurements. This approach reduces overproduction, ensuring that garments are crafted with care and precision for each individual customer, promoting a more sustainable and customer-centric fashion industry.
Conclusion
The fashion industry’s garment production techniques have come a long way, encompassing a rich tapestry of traditions, innovations, and sustainable practices. From the artistry of handcrafted techniques to the efficiency of mechanized processes, and the promise of advanced technologies, each method contributes to the diverse and ever-evolving landscape of fashion manufacturing. As the industry continues to strive for sustainability and ethical practices, embracing a diverse range of production techniques and incorporating eco-friendly materials will be key to creating a responsible and dynamic future for fashion. By making informed choices and supporting sustainable initiatives, both consumers and industry stakeholders can play a pivotal role in shaping a more conscientious and environmentally friendly fashion world.